Nowadays, security is a major issue for any type of application. Increase in large ransomware attacks, traditional passwords are no longer secure. It is recommended to have a few extra layers of security for every account online. Multi-factor authentication provides double security to access any application.
What is Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)?
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is an authentication technique that needs the user to complete two or more verification layers to gain access to a particular resource such as a web/mobile application, online account, Windows PC system, or a VPN connection. MFA is a core component of a strong identity and access management (IAM) policy.
For example, If a user wants to access any application then the user must log in with the first login page using a valid username and password. After that, an additional security factor is visible for a second-time authentication. The system, application, or network will not allow you to access it unless you succeed in getting all these verification right.
There are multiple options for the 2FA
- Push notification on a mobile device
- OTP via SMS
- Mobile applications like Google Authenticator application
- IVRS call
- OTP via Email

There are also hardware type devices for the MFA
- FIDO Security Token
- Hard Token(Time and Event-based)
By using MFA, users are unable to access applications without a valid passcode. Despite one layer breaking, the attacker will still have to take on one or more barriers to gain access which is not an easy job for the attacker.
Why is Multi-Factor Authentication Important?
A major benefit of MFA is that it will enhance your organization’s security by making your users authenticate more than just their username and password. Even though usernames and passwords are important, they can be easily stolen by third parties through brute force attacks. You can be sure that your organization will stay safe from cyber criminals by enforcing MFA factors such as a thumbprint or physical hardware key.
How Does Multi-Factor Authentication Work?
The method of multi-factor authentication involves the use of additional verification information which is also known as factors. The most common MFA factor that users use is one-time passwords (OTP). OTPs are those 4-10 digit codes that you often receive via email, SMS, or mobile app.
With OTPs, a new code is generated periodically or each time an authentication request is submitted. The code is generated based on a seed value that is assigned to the user when they first register. There are multiple ways or implementations to generate the OTPs or provide the second-factor passcode. Here is the list of different MFA Authentication methods that OTPs generate and how users receive those OTPs.
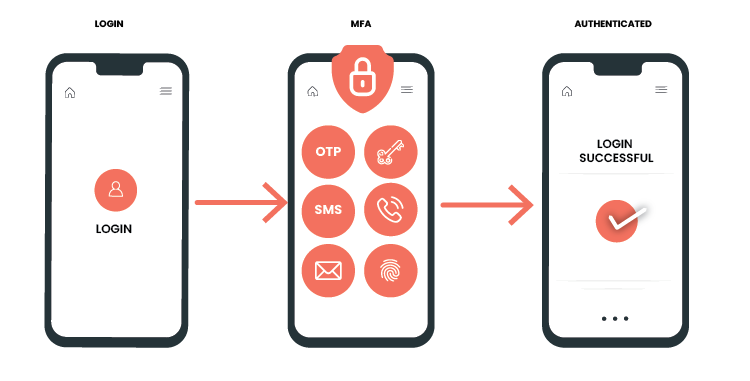
- Authentication using SMS Token: A PIN/Passcode is sent to the user’s registered phone number and then that could be used as a one-time password(OTP)
- Authentication using Email Token: In this method, OTP is sent via Email. This is similar to SMS Token but the only difference is the Passcode is sent via email instead of SMS. For that users should have a registered email ID
- Authentication using Hardware Token: A hardware token is inserted into the device that needs some registration setup and after that, it is used for the authentication. e.g Yubico Security key. Several industries or organizations also use Time-Based(TOTP) and Event-Based(HOTP) Hard Tokens for Authentication
- Authentication using Software Token: In this MFA method, a particular application needs to be installed in the mobile device and after that software token should be inserted/scanned by this application so using that, OTP will be generated
- Authentication via Phone Calls: On the registered mobile number, users can receive phone calls for the OTP
- Authentication via WebAuth or Biometric: In this method, users have some biometric physical hardware devices that have biometric authentication, such as fingerprint ID or facial recognition, and can use this to confirm their identity
Testing Approach for the Multi-Factor Authentication Implemented Systems or Applications
The following approach is useful while testing applications using multi-factor authentication.
- Understand Authentication Solutions: Get what all MFA arrangements coordinate with the application
- Compliance Requirements: See what review prerequisites are being influenced by an MFA implementation
- User Considerations: Get how actualized MFA can affect the different user roles
- Security Requirements: Work along with your security and IT teams to get how MFA adjusts together with your company’s security requirements
- Gadget Necessities: Check in case your company’s versatile gadget arrangements put any limitations on your MFA implementation
Benefits of Multi-Factor Authentication Testing
- Superior Security: Confirmation of the numerous layers of security gives extra assurance to users and companies
- Accomplish Compliance: Achieving compliance measures such as GDPR or HIPPA is necessary to ensure businesses follow strict guidelines that protect consumers’ rights and mitigate risks
- No Information Compromised by Misplaced Devices: Device-based multi-factor verification guarantees that misplaced gadgets don’t lead to compromised data
Multi-factor authentication plays a crucial role in protecting software and applications against malicious activities. To reduce the increasing breach of security, fast-track your MFA implementation in the solution.
Read our case study to know how VOLANSYS help their client with multi-factor authentication implementation.

About the Author: Kalpesh Patel
Kalpesh Patel has been associated with VOLANSYS Technologies for the past 4 years as Senior Engineer in the Engineering division/department. He has vast experience in Automation and MFA domains including Robot Framework, Python, Appium, Selenium, Jenkins (CI/CD), MFA applications.









